Brain Anatomy: Parts, Structure & Functions
Understanding the Brain
Imagine waking up and everything feels normal—but it’s your brain making it all possible. From thoughts and decisions to movements and emotions, this three-pound organ holds the key to everything you do.
Contents
Brain Anatomy: Parts, Structure & FunctionsUnderstanding the BrainKey Takeaways:The Basics of Brain Anatomy: Structure and LayersWhat is Brain Anatomy?The Three Main Parts of the BrainThe Cerebrum: The Powerhouse of Thought and ActionThe Structure of the CerebrumKey Functions of the CerebrumThe Lobes of the CerebrumThe Cerebellum: The Brain’s Balance and Coordination CenterFunction and Location of the CerebellumImpact of Cerebellar DysfunctionThe Brainstem: Your Life Support SystemAnatomy of the BrainstemThe Role of the Brainstem in Life-Sustaining FunctionsBrainstem DisordersThe Limbic System: The Brain’s Emotion CenterAnatomy of the Limbic SystemThe Role of the Limbic System in Emotions and BehaviorLimbic System DisordersThe Thalamus and Hypothalamus: The Brain’s Relay Station and Control CenterUnderstanding the ThalamusThe Hypothalamus – Your Internal Regulator Thalamus and Hypothalamus Disorders The Corpus Callosum: The Bridge Between Hemispheres What is the Corpus Callosum?Function and Importance of the Corpus CallosumDisorders Related to the Corpus CallosumThe Blood-Brain Barrier: Protecting the Brain from HarmWhat is the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)?Challenges with the Blood-Brain BarrierThe Brain and Neuroplasticity: The Ability to Rewire ItselfWhat is Neuroplasticity?How Neuroplasticity Affects Learning and RecoveryThe Role of Brain Anatomy in Neurological DisordersCommon Brain Disorders and Their Anatomical CausesBrain Injury and RehabilitationHow Modern Science and Technology Are Enhancing Brain ResearchAdvancements in Brain ImagingNeurogenetics: Understanding the Genetic Basis of Brain FunctionThe Complexity and Beauty of the BrainCommon Questions
In this blog, we will break down the parts of the brain, their anatomy, structure, and individual functions—showing how each region contributes to your daily experiences, behaviors, and overall health.
Why It’s Important: Understanding the brain anatomy isn’t just for doctors. It helps you grasp how your body works, why you act the way you do, and how neurological issues affect millions globally.
Key Takeaways:
-
- The brain is divided into specialized parts, each responsible for different functions.
- Understanding brain anatomy can improve mental health and treatment outcomes.
- The brain’s structure dictates everything from motor skills to emotions.
- The brain is adaptable and can rewire itself through neuroplasticity.
- Brain research leads to innovative treatments for neurological disorders.
The Basics of Brain Anatomy: Structure and Layers
What is Brain Anatomy?
-
- Definition and the significance of studying brain structure.
- Why understanding how the brain is built is crucial to understanding how it works.
- Overview of key anatomical features: neurons, glial cells, and regions.
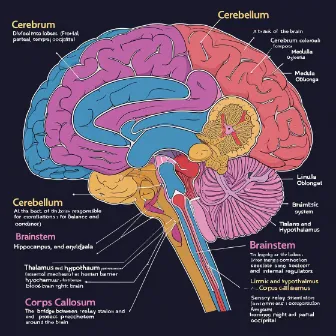
The Three Main Parts of the Brain
-
-
- Cerebrum: The largest part; responsible for higher brain functions like thought, perception, and voluntary movement.
- Cerebellum: Coordination and balance.
- Brainstem: Life-supporting functions such as breathing and heartbeat.
-
The Cerebrum: The Powerhouse of Thought and Action
The Structure of the Cerebrum
-
- The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres: left and right.
- Each hemisphere controls functions in the opposite side of the body.
Key Functions of the Cerebrum
-
- Sensory Perception: Interpreting sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound.
- Higher Cognitive Functions: Reasoning, planning, and judgment.
- Memory and Emotions: Role in both long-term memory storage and emotional regulation.
The Lobes of the Cerebrum
-
- Frontal Lobe: Decision-making, motor control, and personality.
- Parietal Lobe: Sensory processing and spatial awareness.
- Temporal Lobe: Auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory.
- Occipital Lobe: Visual processing and recognition.
The Cerebellum: The Brain’s Balance and Coordination Center
Function and Location of the Cerebellum
-
- Positioned beneath the cerebrum and responsible for fine motor skills.
- Key Roles: Balance, posture, and coordinated movement.
Impact of Cerebellar Dysfunction
-
- Ataxia: Loss of coordination.
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking due to cerebellar issues.
- Disorders that impact cerebellar function (e.g., Cerebellar Ataxia).
The Brainstem: Your Life Support System
Anatomy of the Brainstem
-
- Comprised of the Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata.
- Each part has distinct but critical roles in sustaining life.
The Role of the Brainstem in Life-Sustaining Functions
-
- Breathing and Heart Rate: Essential autonomic functions controlled by the brainstem.
- Reflexes: Automatic reactions like blinking, swallowing, and sneezing.
Brainstem Disorders
-
- Conditions like brainstem stroke, brainstem encephalitis, and their effects on life-sustaining functions.
The Limbic System: The Brain’s Emotion Center
Anatomy of the Limbic System
-
- The hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus are all part of this system.
- They manage emotions, memory, and behavior.
The Role of the Limbic System in Emotions and Behavior
-
- Emotional regulation and the body’s fight or flight response.
- Memory formation and recall, and how emotions shape memories.
Limbic System Disorders
-
- The impact of dysfunction in emotional regulation (e.g., depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder).
The Thalamus and Hypothalamus: The Brain’s Relay Station and Control Center
Understanding the Thalamus
-
- The brain’s sensory relay system that channels all sensory input (except smell) to the appropriate areas of the brain.
The Hypothalamus – Your Internal Regulator
-
- Managing the body’s basic functions: hunger, thirst, temperature, and circadian rhythms.
- Regulating the pituitary gland and controlling hormone release.
Thalamus and Hypothalamus Disorders
-
- Disorders affecting sleep-wake cycles and emotional control (e.g., narcolepsy, hypothalamic dysfunction).
The Corpus Callosum: The Bridge Between Hemispheres
What is the Corpus Callosum?
-
- A bundle of nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
Function and Importance of the Corpus Callosum
-
- Allows for communication between hemispheres for coordinated brain function.
- Facilitates complex activities like speech and movement.
Disorders Related to the Corpus Callosum
-
- Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum (ACC): When the structure fails to develop, leading to coordination and cognitive challenges.
The Blood-Brain Barrier: Protecting the Brain from Harm
What is the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)?
-
- A selective barrier that prevents harmful substances from reaching the brain.
- How it protects the brain from toxins and infections.
Challenges with the Blood-Brain Barrier
-
- The difficulty drugs have in penetrating the BBB and current research on overcoming this barrier.
- New breakthroughs like nanoparticles and gene therapies that aim to bypass the BBB.
The Brain and Neuroplasticity: The Ability to Rewire Itself
What is Neuroplasticity?
-
- The ability of the brain to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections.
How Neuroplasticity Affects Learning and Recovery
-
- Neuroplasticity’s role in learning, memory formation, and post-injury recovery.
- Encouraging neuroplasticity through physical exercise, mental challenges, and therapy.
The Role of Brain Anatomy in Neurological Disorders
Common Brain Disorders and Their Anatomical Causes
-
- How disorders like Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis affect brain structure.
Brain Injury and Rehabilitation
-
- The impact of traumatic brain injury (TBI) on brain function and structure.
- The importance of rehabilitation in promoting recovery and cognitive function post-injury.
How Modern Science and Technology Are Enhancing Brain Research
Advancements in Brain Imaging
-
- MRI, fMRI, and PET scans—cutting-edge tools that help us visualize brain activity and diagnose disorders.
Neurogenetics: Understanding the Genetic Basis of Brain Function
-
- The role of genetics in shaping cognitive functions and susceptibility to brain disorders.
- How technologies like CRISPR are revolutionizing treatment possibilities for brain diseases.
The Complexity and Beauty of the Brain
- Recap the brain’s major parts and their indispensable roles in everyday functions.
- Emphasize the importance of continued research to uncover deeper mysteries of the brain.
- Stay curious, as every discovery about the brain brings us closer to better understanding human nature and treating neurological diseases.
Join the conversation below—what fascinates you most about the brain?
Common Questions
- Q: What are the main parts of the brain?
- The brain consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. These regions control everything from thoughts to basic life functions.
- Q: How does the brain communicate with the rest of the body?
- Through an intricate system of neurons and the central nervous system, the brain sends signals to muscles, organs, and systems for action and regulation.
- Q: Can the brain repair itself after injury?
- The brain can adapt and rewire itself through neuroplasticity, though some severe injuries may cause permanent damage.
- Q: What is the role of the limbic system?
- The limbic system regulates emotions, memory, and behavior. It also plays a role in how we react to stress and emotional stimuli.